Electronic signatures have long been used between parties to bind a contract. However, many people still fear its authenticity and legality. Online transactions and agreements are not free from the risks of fraud, admissibility, repudiation, and compliance. But what are the Legal Issues Concerning Electronic Signatures?
- Proof of Signature – “I didn’t sign this document.”
- Proof of Consent – “This is not the document I signed.”
- Proofing issues – “That has been tampered with!”
- Compliance – “I didn’t see that in the document.”
- Reference – Electronic signatures don’t compare to handwritten signatures on paper.
To answer all the worries, electronic signatures are legal and acceptable in court. Electronic signatures have the same legal weight as signatures made with ink and paper. Considering the auditing processes to make electronic signatures valid, they have even better proof that such signatures happened.
Here are the laws in different countries that made the legal weight of E-signatures stronger:
- USA: E-SIGN Law (for Federal) & UETA Law (for the State) – Learn more here
- United Kingdom: UK eIDAS Regulation – Learn more here
- European Union: eIDAS (Switzerland excluded) – Learn more here
- New Zealand: Electronic Transaction Act – Learn more here
- Australia: Electronic Transaction Act – Learn more here
- Canada: PIPEDA (for Federal) & UECA (for the Province) – Learn more here
How Do Electronic Signatures Seal a Digital Contract?
Electronic signatures are just the same as handwritten signatures, only it is done digitally. When both parties have mutually agreed to the terms and conditions, they will sign the document electronically.
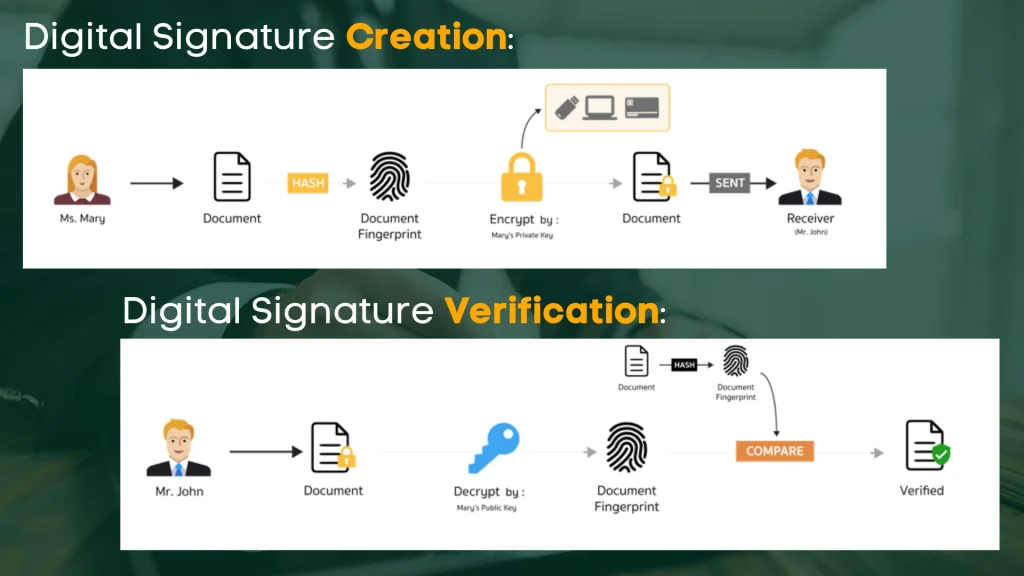
During the signing process, the system will capture the signature by issuing a private and public key. The signee will get to keep this private key. It uses a mathematical algorithm to encrypt this data, then it generates a digital ID or sometimes called a hash for decryption. Any electronic signature that the system cannot read means the signature is invalid.
The law only accepts a valid electronic signature, one that matches the digital key generated by the system, which is always unique to every electronic signature.
There are different forms of electronic signatures:
- By capturing handwritten signatures
- By using a pin or password
- Typing a name
- By telephone keypad
- By responding to an email
- By clicking agreements
It looks like these documents are easily subject to fraud. The answer is no. Unless a signee provides access to the private key to anyone, others can’t use the electronic signature.
So, What Are the Legal Issues Concerning Electronic Signatures?
#1 “I didn’t sign this document.”
Authentication has the most common cause of disputes. When one party claims that the confirmation via electronic signature did not happen, the burden of proof goes with the other party.
Electronic signature providers solved this issue with reliable authentication systems. A well-designed electronic signature system has legal ways to prove intent to sign like:
- Following a series of steps before making the final approval
- Two or three-step authentication
See, a great electronic signature system would ensure that a signee knows about the document he is signing.
Some digital agreements do not proceed to the next page unless the whole page is read, making sure that the signee scrolled down the whole page. There is intent to go to the bottom of the page and click next.
These little things, most signees are unaware of, are valid proof of intent.
#2 “This is not the document I signed.”
Non-repudiation is one party’s denial of the contract’s validity.
Attempted repudiation in contracts can be cases like:
- Not seeing a part of the contract
- The date and time of signing is not inclusive of the date stipulated in the contract.
- Somebody altered the document after signing.
- Having the wrong signatory or not sign
- Changing the contents of the contract without agreement
For a business to avoid disputes and make the contracts valid, the electronic signing system should have a strong audit trail. The system should have very strong documentation and tracking system before and after the capture of the signature. What are the Legal Issues Concerning Electronic Signatures?
These claims can be avoidable if there is an efficient data capture of the signature: generation of digital keys and time stamping.
#3 Proofing issues
In most cases, one cannot tamper with a digitally signed document, and the system will likely invalidate a document when such tampering occurs. The generated hash or digital ID is strong evidence of signing the document and in one way, much stronger than a signed contract on paper.
A signee trying to repudiate his signature will have problems proving he didn’t confirm a transaction or sign a contract. You’ll find these cases in many disputes in online banking transactions. Providing a PIN, password, or OTP will always prove that one has made an approval, confirmation, or agreement.
#4 “I didn’t see that in the document.”
Like any other contract, both parties should comply with the terms and conditions of the agreement. The law requires an organization offering a contract to be fully transparent. Organizations must disclose everything in the paper. There should be no hidden charges or commitments. Especially when it comes to data and privacy, organizations should be transparent on how they are handling the personal information of their clients.
Some exemptions in the law require an organization to disclose consumer consent provisions. These requirements go mostly for financial institutions. It ensures consumers that they can still opt out of the electronic transaction if they wish.
A great way to execute consent is to include fillable questions, showing important disclosures that they understand before clicking confirm or agree in the contract.
#5 Electronic signatures don’t compare to handwritten signatures on paper.
Although e-signatures have the same legal weight as handwritten signatures, there could always be risks. But in most cases, e-signature systems with an established process have a better position in handling these risks than on paper.
Especially when the e-signature system has an excellent audit trail, more organizations rely on their documentation. Both parties have security, and the contracts have fewer questionability.
How to Ensure the Legality and Validity of an E-signature
- Secure proof of intent.
Enhance the authentication process. Use two-way or three-step verification. Banks use one-time-expiring passwords. Document the entire authentication process.
- Secure proof of consent.
Disclose all the terms and conditions in the agreement.
- Secure and protect the e-signature.
Get a reliable e-signature software provider. PKI-based system software is reliable for capturing the signature in the contract. It protects the signed contract with a digital key that’s impossible to copy or modify.
- Both parties must have authentic copies of the contracts.
Just like any contract, send original copies agreed upon by both parties. Every party must have a copy of their own.
The best way to protect e-signatures for both parties is proper documentation, transparency, and most of all, compliance. By doing so, you can declare that both parties have digitally and mutually agreed.