Ever wondered what makes your computer tick? At the heart of this technological marvel lies the motherboard, quietly managing the chaos of circuits and connections that bring your device to life.
Think of the motherboard as the central hub, the maestro orchestrating the symphony of your computer’s components. In this article, we break down the definition of a motherboard, introduce you to its key components, and shed light on the crucial functions it performs. Whether you’re a tech novice or an aspiring guru, join us on this journey to demystify the motherboard and grasp the essential role it plays in powering your digital world.
Curious about the magic behind your computer’s operation?
We unravel the mystery of the motherboard – the central hub where all the action takes place. From sockets to traces, we break down the components that make this powerhouse tick. Whether you’re a tech aficionado or just getting started, the journey into the motherboard promises a deeper understanding of your digital companion.
Imagine having the key to unlock the secrets of your computer’s core functionality. By the end of this article, you’ll not only know what a motherboard is but also appreciate the vital role it plays in shaping your digital experience. Get ready to desire a newfound understanding of the tech that surrounds you every day.
Take the plunge into the world of motherboards and emerge with a deeper appreciation for the technology that powers your digital world, Read on!
Did you know?
- Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the global Motherboard market size is estimated to be worth USD 13290 million in 2022 and is forecast to a readjusted size of USD 14670 million by 2030 with a CAGR of 1.4Percent during the forecast period 2023-2030.
- Global Motherboard key players include Asus, Gigabyte Technology, Micro-Star International Co., Ltd, etc. Global top three manufacturers hold a share over 25 percent.
Introduction to Motherboards: Unveiling the Core of Your Computer
Welcome to the gateway of your computer’s inner sanctum – the motherboard. Often operating behind the scenes, the motherboard is the central nervous system of your device, seamlessly connecting and coordinating all its components. Think of the motherboard as the epicenter, where the processor, memory, storage, and various peripherals converge to harmonize and execute your digital commands.
Defining the Motherboard: Decoding its Fundamental Role
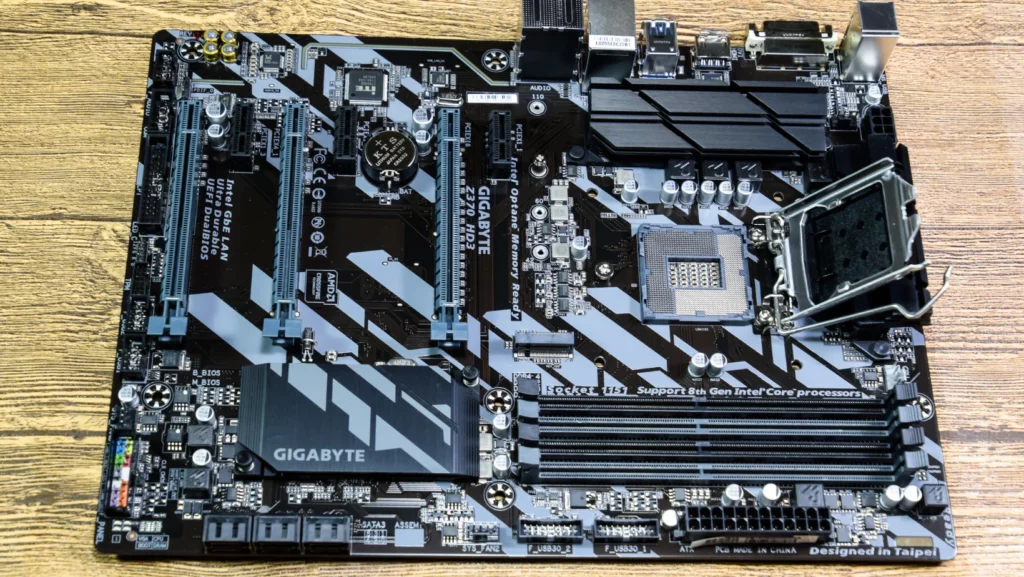
The motherboard is the central piece of hardware in your computer, acting as the primary hub that connects and facilitates communication between various essential components. Its fundamental role is akin to the nervous system of the computer, overseeing the seamless coordination of data flow and instructions.
At its core, the motherboard provides a home for the CPU (Central Processing Unit), the brain of the computer. The CPU carries out instructions, performing calculations and tasks that drive the overall functionality of the system.
Here are some of its fundamental roles:
Central Hub of Operations:
The motherboard is the ultimate traffic controller of your computer, directing data and instructions between all its parts – from the processor to the memory and beyond.
Home for the CPU:
At its core, the motherboard provides a cozy socket for the Central Processing Unit (CPU), the brain of your device. It’s where the magic happens, with the CPU carrying out the instructions that keep your computer running.
Memory Matters:
Ever wonder where your computer stores its short-term memory? The motherboard hosts the RAM (Random Access Memory), ensuring your device can swiftly access and retrieve data for quick, on-the-fly tasks.
Storage Connection Point:
Your hard drive or SSD needs a home too, and that’s where the motherboard’s storage connectors come in. They provide the link between the motherboard and your long-term storage, allowing seamless access to your files.
Peripheral Playground:
From USB ports to audio jacks, the motherboard offers an array of connectors for your peripherals. It’s the welcoming host that ensures your keyboard, mouse, and other devices can communicate effortlessly with your system.
Expansion Slots for Growth:
Need to beef up your system with additional capabilities? The motherboard boasts expansion slots, where you can add graphics cards, Wi-Fi adapters, and more to enhance your computer’s performance.
In essence, the motherboard is the architectural foundation of your computer, bringing together all its essential components to create a cohesive and functional system.
Building Blocks: Essential Components of a Motherboard
In the exploration of a motherboard’s anatomy, understanding its essential components is crucial. These building blocks collectively form the backbone of the motherboard’s functionality:
CPU Socket:
The central processing unit (CPU) socket is like a tailored seat for the brain of your computer. It’s a designated space on the motherboard where the CPU is securely placed, allowing it to communicate with other parts of the system.
RAM Slots:
Random Access Memory (RAM) is the short-term memory where your computer stores data for quick access. RAM slots on the motherboard provide the housing for these memory modules, allowing for quick retrieval and processing of data.
Expansion Slots:
Motherboards come with expansion slots to accommodate additional components like graphics cards, Wi-Fi cards, or other expansion cards. These slots provide the means to enhance your system’s capabilities.
Storage Connectors:
The motherboard features connectors for storage devices like hard drives and solid-state drives. These connectors establish a link between the motherboard and your long-term storage, facilitating data access and retrieval.
Chipset:
Acting as a communication manager, the chipset is a set of integrated circuits on the motherboard. It enables smooth communication between the CPU, RAM, storage, and other connected peripherals.
BIOS/UEFI:
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is firmware embedded in the motherboard. It initializes the essential hardware components during the boot process, ensuring your computer starts up correctly.
Understanding these building blocks provides insight into how a motherboard functions as a cohesive unit, orchestrating the intricate dance of data and instructions that powers your computer.
The 7 Important Functions of a Motherboard
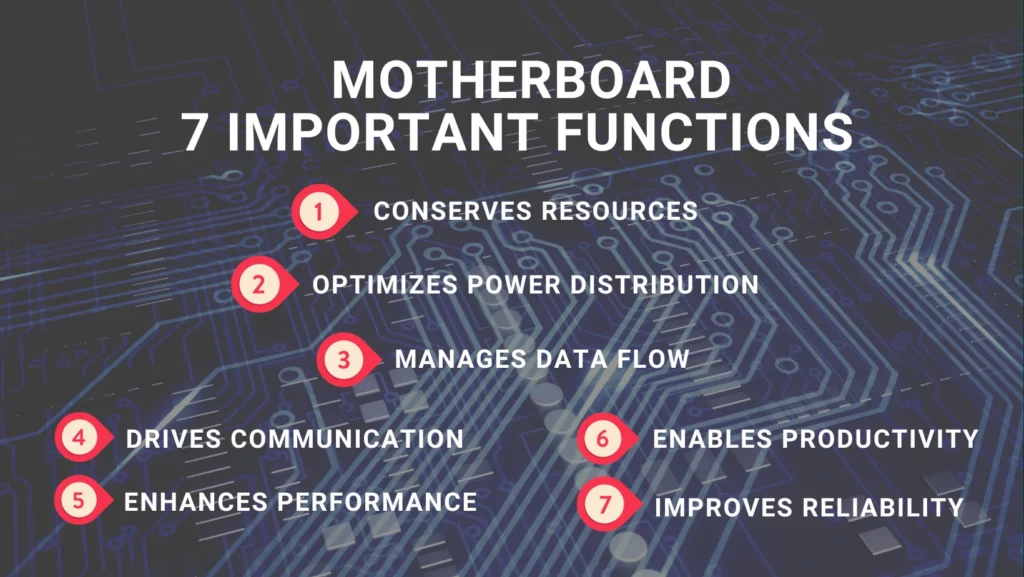
Let’s delve deeper into the seven important functions of a motherboard:
1. Manages Data Flow:
The motherboard acts as a central hub for data flow within a computer. It coordinates the transfer of information between the CPU, memory, storage, and other connected components, ensuring a smooth and efficient exchange of data.
2. Conserves Resources:
Effectively managing system resources is a critical function of the motherboard. It allocates and prioritizes resources such as CPU time, memory space, and bandwidth to various tasks, optimizing overall system performance.
3. Optimizes Power Distribution:
Power distribution is a key responsibility of the motherboard. It regulates and optimizes the distribution of electrical power to different components, preventing power-related issues and ensuring that each part receives the appropriate voltage.
4. Drives Communication:
Facilitating communication between components is fundamental to the motherboard’s role. Through various connectors and buses, it enables devices like USB peripherals, graphics cards, and networking components to communicate seamlessly with the CPU and each other.
5. Enhances Performance:
The motherboard plays a pivotal role in enhancing overall system performance. It provides expansion slots for additional components, allowing users to upgrade their systems with graphics cards, sound cards, or other peripherals that can boost performance.
6. Improves Reliability:
Reliability is a cornerstone of the motherboard’s function. By ensuring stable connections, efficient power delivery, and proper resource allocation, it contributes to the overall reliability and longevity of the computer system.
7. Enables Productivity:
Ultimately, the motherboard enables productivity by creating a stable and efficient platform for computing tasks. Its functions contribute to a smooth user experience, allowing individuals to work, play, and engage with their devices without interruptions.
The motherboard acts as the backbone of a computer, managing data, conserving resources, optimizing power distribution, driving communication, enhancing performance, improving reliability, and enabling overall productivity in the digital realm.
Motherboards and Compatibility: Tips for Choosing the Right Fit

Choosing the right motherboard is a critical step in building a computer. Here are some tips to help you make an informed decision:
- CPU Compatibility: Ensure that the motherboard supports your chosen CPU. Check for the specific socket type and verify compatibility with the processor generation you plan to use.
- Form Factor Consideration: Match the motherboard’s form factor with your computer case. Common form factors include ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. Ensure that the motherboard fits into your case properly.
- RAM Compatibility and Capacity: Check for the supported RAM type, speed, and maximum capacity. Ensure that the motherboard can accommodate the amount and type of RAM you plan to use for optimal performance.
- Expansion Slots and GPU Support: Consider the number and type of expansion slots. If you plan to use a dedicated graphics card, ensure that the motherboard has the appropriate PCIe slot and provides sufficient clearance for the GPU.
- Storage Options: Verify the storage connectors available on the motherboard. Check for SATA ports for traditional hard drives and SSDs, as well as M.2 slots for NVMe SSDs. Ensure compatibility with your storage preferences.
- Connectivity Ports: Consider the number and types of USB ports, audio jacks, and networking options provided by the motherboard. Ensure that it has the connectivity you need for your peripherals and networking requirements.
- Power Delivery and Overclocking Support: If you plan to overclock your CPU, ensure that the motherboard has robust power delivery components. Check for features like heatsinks on the VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules) for efficient heat dissipation.
- BIOS/UEFI Features: Look for motherboards that offer user-friendly BIOS or UEFI interfaces. Having a motherboard with easy BIOS updates and a user-friendly interface can simplify system management and troubleshooting.
- Build Quality and Brand Reputation: Consider the overall build quality of the motherboard and the reputation of the manufacturer. Established brands with a good track record for reliability and customer support are often a safer choice.
- Future-Proofing: Think about future upgrades. Choose a motherboard that provides room for expansion and upgrades, considering potential advancements in technology and your future computing needs.
- Budget Consideration: Set a realistic budget and find a motherboard that offers the features you need within that budget. Avoid overspending on features you won’t utilize.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select a motherboard that aligns with your specific requirements, ensuring a stable and efficient foundation for your computer build.
Future-Proofing with Motherboards: Navigating Technological Evolution
As technology rapidly evolves, future-proofing your computer begins with selecting a motherboard that can seamlessly adapt to upcoming advancements. The choice of a versatile CPU socket is paramount, allowing for easy upgrades to the latest processors without the need to replace the entire motherboard.
Expansion slots play a crucial role in accommodating future hardware, providing the flexibility to integrate additional components such as advanced graphics cards or emerging peripherals. To ensure your system stays on the cutting edge, prioritizing memory capacity and speed is essential. Opting for a motherboard that supports higher RAM capacities and faster speeds enables smooth upgrades for memory-intensive applications and upcoming software requirements.
Connectivity is another key aspect of future-proofing. Choosing a motherboard with the latest USB standards, including USB-C and Thunderbolt support, ensures compatibility with evolving peripherals and data transfer technologies. M.2 slots for NVMe SSDs contribute to future storage advancements, enhancing overall system performance. Additionally, considerations for Wi-Fi standards and Ethernet technologies anticipate faster internet speeds and improved network connectivity.
A motherboard’s ability to receive timely BIOS or UEFI updates is vital for adapting to new hardware releases and unlocking features introduced by the manufacturer. Overall, a well-informed choice in motherboard selection lays the foundation for a system that can seamlessly navigate technological evolution and remain relevant in the fast-paced world of computing.
Frequently Asked Questions About What Is a Motherboard: Definition, Components, and Functions
Q: What is a motherboard, and why is it important in a computer?
A: A motherboard is the main circuit board in a computer that connects various components, such as the CPU, memory, storage, and peripherals. It serves as the central hub for communication and power distribution, making it a crucial component of a computer’s functionality.
Q: What are the essential components of a motherboard?
A: Key components of a motherboard include the CPU socket, memory slots, expansion slots (PCIe), storage connectors (SATA, M.2), power connectors, and various ports for USB, audio, and networking. These elements work together to facilitate the functioning of the entire system.
Q: How do I know if a motherboard is compatible with my CPU?
A: Check the CPU socket type on the motherboard and ensure it matches the socket type of your CPU. Additionally, verify if the motherboard supports the specific generation of your processor, as compatibility can vary.
Q: What is the role of the BIOS or UEFI in a motherboard?
A: The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is firmware embedded in the motherboard. It initializes hardware during the boot process, manages system settings, and allows users to configure parameters. It plays a crucial role in the system’s startup and overall functionality.
Q: How does the motherboard contribute to system performance?
A: The motherboard facilitates communication between components, manages data flow, and optimizes power distribution. It also provides expansion options for upgrading components like graphics cards and supports high-speed memory and storage, contributing to overall system performance.
Final Thoughts
In the world of computers, the motherboard is like the central hub, connecting all the parts and making sure they work together harmoniously. Comprised of essential components such as the CPU socket, memory slots, and various connectors, its role is to ensure that your computer’s brain (CPU), memory, and storage communicate effectively.
Think of it as the conductor in an orchestra, directing each instrument (component) to play in sync. The motherboard’s job doesn’t stop there—it manages power distribution, initializes hardware during startup, and lays the groundwork for your computer’s overall performance.