In a world driven by technological advancements, a remarkable feature has quietly revolutionized how we interact with our devices and surroundings—NFC tags. These unassuming, tiny wonders hold immense potential for simplifying our lives, from enabling contactless payments to automating everyday tasks.
Today, we’ll delve into NFC (Near Field Communication) tags, exploring their functionality and how they work to bridge the gap between physical and digital domains.
We’ll break this topic down into several sections to provide a clear understanding of what NFC tags are and how they make our lives easier.
Have you ever heard of NFC tags and wondered what they are?
Near field communication (NFC) tags are small electronic devices, typically powered by a battery-less chip, that can store data such as URLs, numbers, text strings, or commands, allowing them to communicate with nearby mobile devices with an NFC reader installed. These NFC tags can be found in various shapes and sizes to fit any application you might need them for.
Smartphones now have built-in support for reading and writing these types of tags, which makes interacting with objects as simple as tapping your phone against it! You can use NFC tag technology to provide customers with more streamlined products & services like making payments at retail outlets or quickly connecting to a WiFi network by placing their device next to an NFC tag instead of manually entering all the information each time. No longer will customers need to worry about forgetting passwords – tap & go!
What are NFC tags?

NFC tags, short for Near Field Communication tags, are small passive devices capable of wirelessly storing and transmitting data to NFC-enabled devices like smartphones or tablets. These tags, often embedded in objects, stickers, cards, or wearables, facilitate seamless communication when brought into proximity or touched by an NFC-enabled device.
Comprising an integrated circuit (IC) and an antenna, NFC tags possess a limited storage capacity for data such as URLs, contact information, or commands. When an NFC-enabled device approaches the tag, the device’s NFC chip generates a small electromagnetic field that powers the tag, enabling the IC to transmit stored data back to the device.
NFC tags can be programmed with specific information using NFC-enabled devices, giving them varied capabilities. For example, an NFC tag can carry a website URL, and tapping an NFC-enabled device on the tag opens the linked webpage. These tags find use in mobile payments, access control systems, advertising, and product authentication, providing convenient, contactless experiences and seamlessly linking the physical and digital worlds.
How do NFC tags work?
NFC tags employ short-range wireless communication between the tag and an NFC-enabled device, such as a smartphone or tablet. These small, passive devices have an integrated circuit (IC) attached to an antenna.
When an NFC-enabled device is brought close to an NFC tag (usually within a few centimeters), it generates a small electromagnetic field. This field powers the NFC tag by inducing an electric current in its antenna. As a result, the IC within the tag becomes energized and ready to communicate.
Once powered, the NFC tag can transmit data to the NFC-enabled device. The IC modulates the energy from the device’s electromagnetic field and sends a response signal carrying the stored data. This signal is received by the NFC chip in the device, which then processes the data accordingly.
NFC tags may hold multiple types of data, including URLs, contact information, and commands. Using an NFC-enabled smartphone, they can be programmed or written with specific data. This process can be done via dedicated mobile apps or built-in operating system functions.
NFC tags: How to Read and Write Data?
NFC tags provide a versatile platform for storing and transmitting data wirelessly. The ability to read and write data to NFC tags opens up possibilities for customization and interaction.
Now, let’s explore how to read and write data on NFC tags. This helps users program these tags with specific information and access that data with NFC-enabled devices. By understanding the process of reading from and writing to NFC tags, you can harness the full potential of these powerful little devices.
Reading from NFC tags
To read data from an NFC tag, follow these steps:
- Ensure that your NFC-enabled device has NFC functionality enabled.
- Bring your device close to the NFC tag, allowing the NFC chip and antenna to generate an electromagnetic field.
- The NFC tag will absorb power from the device’s field, activating the integrated circuit (IC) within the tag.
- The IC then transmits the stored data back to the NFC-enabled device.
- The device’s NFC chip receives the data and makes it available for processing by applications or operating system features.
Writing data to NFC tags
To write data to an NFC tag, follow these steps:
- Ensure your NFC-enabled device has NFC functionality enabled.
- Use a compatible application or operating system feature to initiate the writing process.
- Place the NFC tag within your device’s NFC chip and antenna.
- The NFC-enabled device generates an electromagnetic field to power the NFC tag.
- The writing process involves programming the desired data onto the NFC tag, such as URLs, contact information, or commands.
- Once the writing process is complete, the data is stored on the NFC tag and can be accessed by other NFC-enabled devices.
Note that the steps for reading from and writing to NFC tags may vary depending on the device and the software used. However, the underlying principle remains: the NFC-enabled device establishes communication with the NFC tag through an electromagnetic field, enabling data transmission in both directions.
Users can customize NFC tags by reading from and writing to suit their needs – storing contact information, launching specific actions, or facilitating seamless interactions with the digital world.
Secure, Standardized, and Regulated Technology
NFC tags are not only a powerful technology, but they are also secure, standardized, and regulated, providing users with peace of mind. Let’s dive into why NFC tags are considered such a reliable and trusted platform:
Security
Security is a top priority when it comes to NFC tags. These tags support encryption protocols, ensuring secure communication between devices and NFC tags. Encryption protects sensitive data, and the risk of unauthorized access or interception decreases.
Standardization
One of the key advantages of NFC technology is its standardization. The NFC Forum, an international consortium of companies, has established global standards for NFC. These standards promote interoperability and compatibility among NFC-enabled devices and NFC tags worldwide. This means that regardless of the device or tag manufacturer, NFC technology works seamlessly, providing users with a consistent and reliable experience.
Regulations
In addition to standardization, NFC tags also comply with strict regulations. For instance, when NFC is used for contactless payments, it adheres to regulatory frameworks set by financial institutions, card networks, and payment schemes. These regulations ensure security, privacy, and consumer protection for trustworthy transactions. NFC tags used in payment applications often undergo rigorous certification processes to meet industry standards and security requirements.
It provides a secure, standardized, and regulated platform combining security measures, global standards, and regulatory compliance. NFC tags provide customers and organizations with a dependable solution for facilitating secure money transactions, enabling access control systems, and ensuring authentication processes.
Convenient and Affordable Technology
NFC (Near Field Communication) tags have gained popularity for their secure and standardized nature and inherent convenience and affordability. Let’s explore why NFC tags are considered a convenient and cost-effective technology:
Convenience
- Ease of use: NFC tags offer a user-friendly experience with a simple tap or touch. Users can interact with NFC tags by bringing their NFC-enabled device close to the tag. This straightforward interaction eliminates the need for complex pairing processes or manual data input.
- Seamless integration: NFC technology is integrated into various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and wearables. This widespread adoption ensures that NFC-enabled devices are readily available, allowing users to interact with NFC tags using their existing devices conveniently.
- Versatile applications: NFC tags are programmable with different data types, such as website URLs, contact information, or commands. This versatility allows NFC tags to be used in various scenarios.
Affordability
- Cost-effective solution: NFC tags are relatively inexpensive compared to wireless communication technologies. Their affordability makes them suitable for various use cases, including small-scale applications or large-scale deployments. This affordability factor encourages the wider adoption of NFC technology.
- Longevity and reusability: NFC tags are durable and have a long lifespan. They can withstand various environmental conditions and frequently use, ensuring reliable performance. NFC tags can be rewritten or reprogrammed multiple times, allowing for flexible use and cost savings.
What do phones use NFC for?
The smartphone in your pocket (or hands) uses NFC technology in many ways. Here’s a brief list summarizing what phones use NFC for:
- Contactless payments: NFC-enabled phones can be used for secure and convenient contactless payments by linking them to mobile payment services such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, or Samsung Pay.
- Mobile ticketing: NFC technology allows phones to store and validate digital tickets for various events, transportation systems, concerts, movies, and more.
- Access control: To enter secure areas, buildings, or hotel rooms by tapping your phone on compatible NFC readers.
- Data transfer: For sharing contact information, photos, videos, or other small files by bringing the devices close together.
- Mobile marketing and advertising: NFC tags embedded in posters, advertisements, or product packaging can be tapped by NFC-enabled phones.
- Bluetooth pairing: By tapping an NFC-enabled phone on an NFC-enabled speaker, headset, or another Bluetooth device, they can quickly establish a Bluetooth connection.
- Loyalty programs: Store and redeem loyalty cards or reward points at participating retailers or establishments.
- Public transport: Contactless payment systems for public transportation to pay for fares by tapping phones on NFC readers at ticket gates or terminals.
- Smart home integration: Control and interact with NFC-enabled smart home devices, such as door locks, thermostats, lights, and home entertainment systems.
- Authentication and security: Secure authentication processes, such as two-factor authentication or unlocking devices with NFC-based security tokens or tags.
How are Businesses using NFC tags?
Here’s a list of things businesses are doing using NFC tags:
- Contactless payments and transactions.
- Streamlining mobile point-of-sale (mPOS) systems.
- Enhancing customer loyalty programs and rewards.
- Interactive marketing and advertising campaigns.
- Simplifying access control and security systems.
- Streamlining inventory management and tracking.
- NFC-based product authentication and anti-counterfeiting.
- Benefits of using NFCs
Benefits of Using NFCs
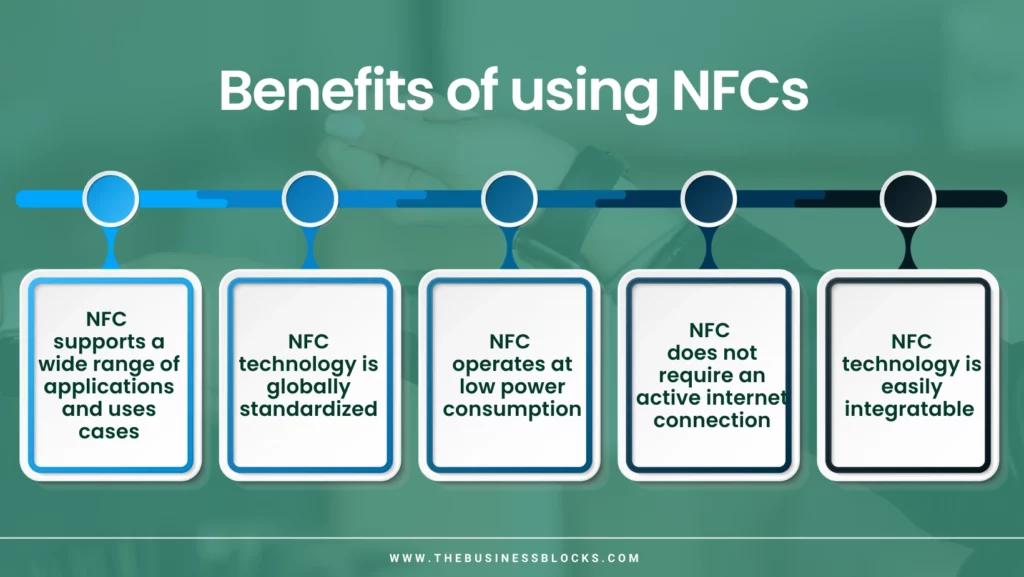
NFC tags’ ease, convenience, and security are their self-explanatory benefits. However, there are some not-so-obvious benefits of NFCs as well:
- NFC supports a wide range of applications and uses cases, making it a versatile and useful technology for almost all sectors
- NFC technology is globally standardized, ensuring interoperability between different devices and systems from different manufacturers
- NFC operates at low power consumption, making it energy-efficient and suitable for battery-powered devices
- It does not require an active internet connection for basic functions like contactless payments or accessing stored information.
- NFC technology can be easily integrated with existing infrastructure, systems, and devices
As you program NFC tags or blank NFC tags and format smart tags, remember that almost any NFC device can read the data stored on these tags. Use secure protocols when transferring sensitive information, and always consider your customer’s privacy needs when setting up transactions!
NFC technology is becoming increasingly popular, so now is a great time to get familiar with how it works and start leveraging its power for your business. With the right setup, you can save time and money while providing a more convenient experience to customers.
Frequently Asked Questions about What Are NFC Tags and How Do They Work?
How do I write data to an NFC tag?
Using dedicated NFC apps or settings, you can write data to an NFC tag using a compatible NFC-enabled device, such as a smartphone.
Can any smartphone read NFC tags?
Most modern smartphones with NFC capabilities can read NFC tags, but checking the device’s specifications is always good to ensure compatibility.
Are NFC tags reusable?
NFC tags vary—some are read-only, while others can be rewritten or formatted for reuse.
What is the maximum storage capacity of an NFC tag?
The storage capacity of an NFC tag can vary, but typical NFC tags have storage capacities ranging from a few kilobytes to several megabytes.
What is the difference between the RFID tag and the NFC device?
RFID tags are passive devices that don’t require a battery but rely on nearby readers to provide the energy needed to read and write data. On the other hand, NFC devices are active devices that use their internal power supply and can be programmed in various ways – from accessing services to sending commands.
Conclusion
NFCs are here, both the present and future of wireless communication and transaction. We hope this brief guide has educated you on the basics of NFC technology, its use cases, and its benefits. So how does NFC work? Simply put, it’s a type of wireless communication that allows two devices to quickly and securely NFC data exchange over short distances.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology is used to power NFC tags and works by emitting a radio signal that contains the tag’s data. NFC readers transfer data and can pick up this signal, read the encoded data, and then transfer that information over a secure connection to an application or service for processing. NFC devices are incredibly versatile and can be used for various applications.