In today’s world, it is more important than ever before to have a secure website. From major corporations to small businesses, having a safe and secure site is imperative. You might be wondering what exactly an SSL Certificate does for you and why you should use them on your website. This article will teach you all about the benefits of using an SSL Certificate and how they work!
What is an SSL Certificate?
And why should I install it on my website?
An SSL Certificate is an encryption that ensures the safety of the user’s information on the website. These e-commerce transactions include anything from transactions with credit cards or online purchases, etc.
They are issued by a certification authority (CA). A Certification Authority is a trusted third party that verifies the identity of websites using SSL certificates. The CA also issues the digital certificate to secure the website or domain, so it’s important to choose an authority you can trust with your security needs.
Why are SSL Certificates important?
A few years ago, Google began considering HTTPS as a factor in search rankings to encourage more website owners to use SSL certificates. Security metrics estimate that about 40% of all page loads were encrypted in 2018 worldwide, up from 30% just a year prior. These numbers will likely continue to grow given the incentives created by recent changes at major browsers.
Websites that are not using them are vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks, which can lead to passwords and login information being intercepted when you’re typing them on the site. Since the information is intercepted while it’s being transmitted, a hacker can pretend to be a website and get you to give up your login information.
SSL Certificates are important because they protect your website and its users from hackers. Many believe that SSL Certificates are needed for e-commerce sites in particular, but in reality, they are essential for any site. SSL Certificates also assure your customers that you take their information seriously and want to be the best at making sure they are safe when buying products or filling out sensitive forms.
What are the benefits of using an SSL Certificate?
Do I really need an SSL certificate? The answer is absolute yes! You should never run your website without one. For example, problems may arise if you are running PayPal’s payment platform on your site and haven’t purchased an SSL certificate.
PayPal has been requiring that all website transactions be conducted via SSL since September 30, 2016. If your site is not using the secure protocol name (e.g., https://), and when a customer makes an authorization or payment on your webpage, they will receive an error message, which may also prevent them from completing their purchase in some cases.
Suppose you have a lot of sensitive information being transferred between your server and the client’s computer; in that case, it is always better to use an SSL Certificate because it encrypts all of that data so that hackers can’t steal private information.
As you probably already know, all users should type in https:// instead of just https:// before entering a website address into the browser. This is to ensure that people are getting encrypted connections between their browser and your web server, which protects them from prying eyes.
Unfortunately, even though it might seem like the user is on your website, they are actually not. Nefarious hackers are trying to intercept any information people might be sending to you, so you should always use an SSL Certificate.
How do they work?
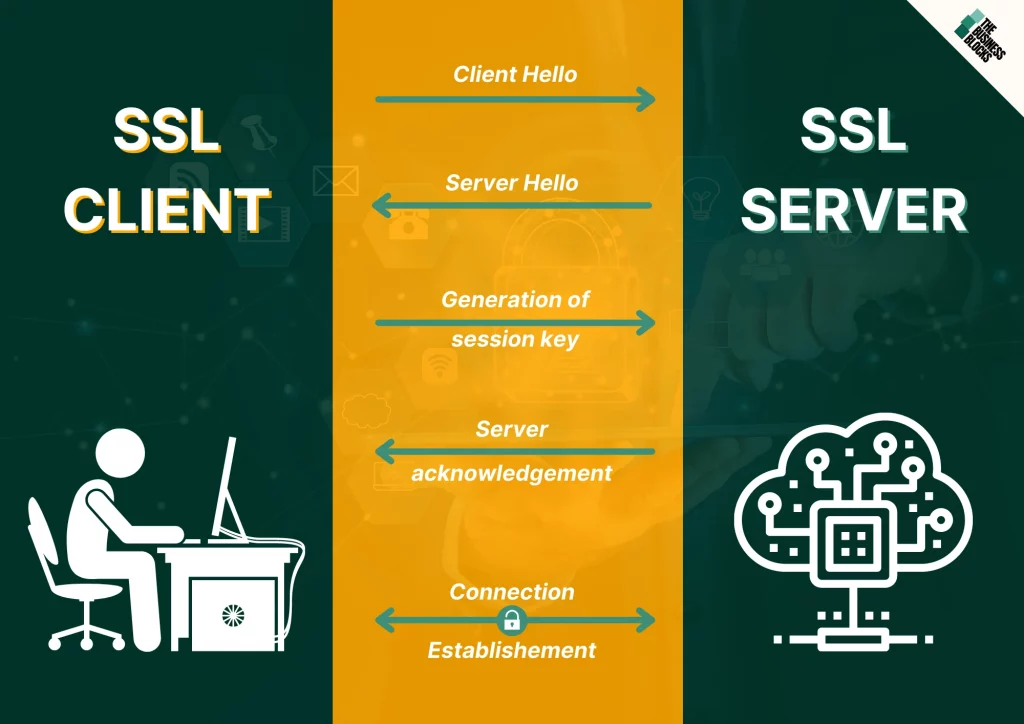
SSL, or Secure Socket Layers, are cryptographic protocols that allow sensitive data to be transmitted securely over the internet. No one will be able to intercept this communication between you and your customers or partners.
Ensure trust in communication with your web visitors by using encryption. SSL Certificates secure your website by encrypting sensitive data sent between the user’s browser and your website. Without this encryption, personal information such as credit card numbers can be intercepted by other nearby computers or other networks that the user is connected to.
The primary function of these certificates is to authenticate the user’s identity or encrypt online transactions. Specifically, this means ensuring that the user is who he claims to be and that he has not been intercepted en route. This way, you can ensure secure connections with your users and partners without worrying about it being compromised by hackers trying to get a hold of their personal information or resources.
In addition to establishing a secure connection, certificates also need to identify the website’s company and domain name. Any information passing through SSL will be encrypted and unreadable for hackers. Still, if it were to go through without an SSL Certificate (that is, with the wrong details) the data would be visible and potentially used by fraudsters or malicious users.
How much does it cost to purchase a certificate?
A typical SSL Certificate, including both the installation and the first year’s maintenance/renewal, costs between $5 and $1,000 per year. Fortunately, you can avail of free SSL certificates, and it sometimes comes with your hosting plan.
How can I get a free SSL Certificate?
There are a lot of companies that offer free certificates, but you want to make sure the company is reputable and has been in business for years. If you are serious about your website, it is vital to invest in a company that will provide secure certificates.
You can find free SSL certificates on the following websites:
SSL For Free – https://www.sslforfree.com/
Let’s Encrypt – https://letsencrypt.org/
CloudFlare – https://www.cloudflare.com/ssl-x/
ZeroSSL – https://zerossl.com
All of these companies will provide you with a free SSL Certificate, but make sure to read the terms and conditions before signing up with them. Make sure you select an appropriate option for your website’s security needs; some certificates might be better than others in certain situations (e.g., if it is for e-commerce).
Their services are not meant specifically for one use case, but rather give options depending on what kind of website you have and how long you want your certificate to last (1 month – 1 year).
Some hosting companies offer free ones for websites running on WordPress, such as Siteground, TMDHosting, Bluehost, etc.
Free certificates from Let’s Encrypt have been particularly effective at increasing the number of secure sites on the web since so many websites don’t bother with encryption.
If you prefer to pay for your SSL Certificate, then you can buy one from these companies:
- Comodo: Comodo is very affordable. They offer certificates for as low as $7.07/year. They also provide a 30-day money-back guarantee.
- GeoTrust: GeoTrust is one of the most popular SSL Certificate providers, so many trust them with their website security. They offer OV certificates as well as EV products. You can avail of one for $87/year.
- Thawte: Thawte has been one of the early pioneers in SSL security and has been providing trustworthy certificates since 1994. Their certificates come at a lower cost than other providers, making them attractive to buyers. They offer certificates for $47/year.
When should I purchase an SSL certificate?
So, if your website is dealing with any type of user or customer information, it’s a good idea to have on on the site. Most online stores will want to use them as well as banks and other financial institutions.
What are the different types of SSL Certificates?
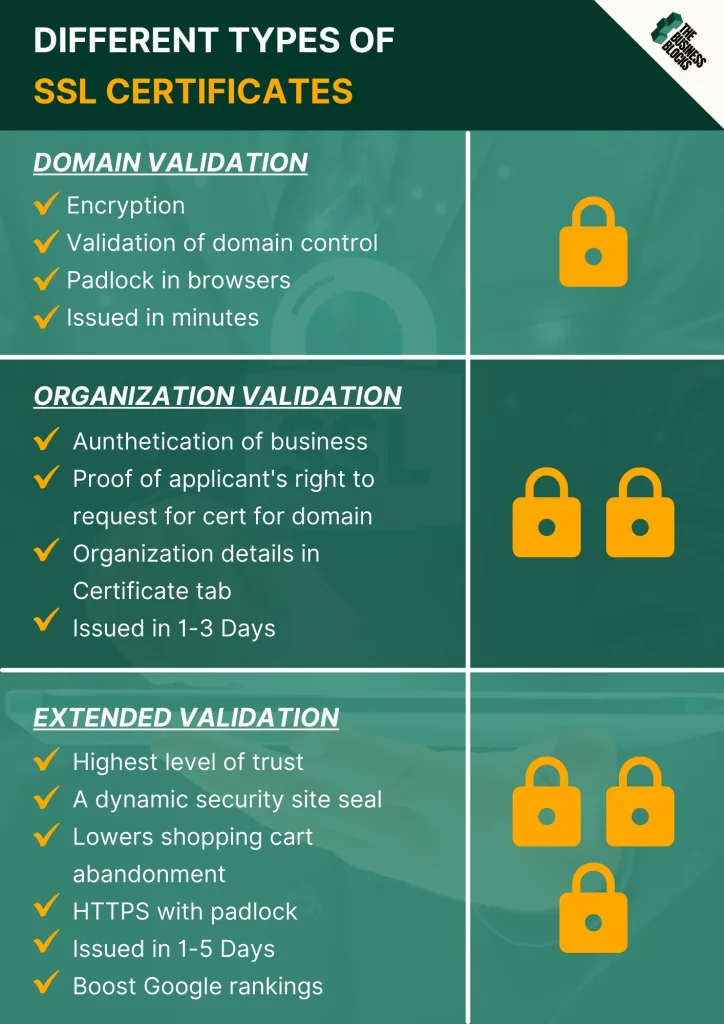
There are three different types of SSL Certificates: Domain Validation, Organization Validation, and Extended Validation.
Domain Validation certificates only require the company to prove that it owns its domain, but they do not verify who is submitting the request, or if that person is authorized to request a certificate.
Organization Validation certificates require the company requesting the certificate to provide proof that they are in charge of the domain name in question. This type of certificate also requires the company to submit name evidence, an email address, fax number, physical address, government-issued identification card, in addition to their domain ownership information.
Extended Validation certificates are comparable with Organization Validation certificates because they will both require extensive validation before issuing a certificate. The difference is that extended validation will require company-issued certificates, which prove that a user is accessing a real website.
There are other types of SSL certificates based on the number of domain names or subdomains.
Wildcards are also known as Universal SSL certificates. The Wildcard SSL is effective for any name and/or type of domain that you require.
A Wildcard SSL Certificate can secure any number of subdomains with one single certificate. These certificates are very economical for business owners who own several websites or domains that share the same registrar or host.
Multi-domain SSL certificates are also known as Unified Communications (UC) SSL certificates. These types of certificates can secure any number of domains, but they cannot secure individual subdomains. UC SSL certificates are suitable for companies with many domains that they want to secure at different levels of validation.
A single-domain SSL certificate is the best option for individual websites and small businesses. A single-domain SSL certificate secures a single domain and its associated subdomains, such as blog.domainname.com and server.domainname.com.
How can you detect if someone is using an invalid SSL Certificate on their website?

If you want to know if someone is using an invalid SSL Certificate on their website, then refer to the following ways:
First, check for a padlock in the URL address. If it’s there, then it has been verified by a certificate chain authority, and you can trust that they are using a valid certificate.
Second, look at the domain name. If the name does not show “https,” then it likely doesn’t have an SSL certificate installed, and you should be wary of putting your information there.
What happens if I don’t have a valid SSL certificate on my site?
If your site doesn’t have a valid Certificate, hackers may be able to take advantage of this vulnerability and intercept sensitive data. Any person who visits your website may also be at risk if visitors use an outdated browser or not use the latest security settings.
Also, if you don’t have a valid certificate on your site, the users will be notified that something is wrong with the site’s security when trying to access it. They can also see an invalid address in the URL field or get other warnings issued by their browser. Your website looks suspicious and untrustworthy, which results in loss of visitors and loss of money.
Do SSL Certificates expire?
Yes, they do expire. They have a validity period, but it’s just as important for you to know when they expire so that your security doesn’t suffer. It is recommended that SSL Certificates be renewed at least every two years.
If your SSL Certificate expires, any sensitive information exchanged through it becomes unreadable to third parties because the certificate has become invalid. When you enter personal information on websites with expired SSL Certificates, hackers can easily steal it because they can read what was being sent across the internet in plain text.
As time goes on, SSL Certificates are becoming more and more popular because they play an important role in cyber security. Many different websites use them, including social media sites, e-commerce stores, and personal blogs.
Small business owners often overlook the importance of SSL Certificates, but their benefits far outweigh the cost. With an SSL Certificate, you can protect sensitive information from being stolen and your website from being hacked or impersonated.
As with anything, it may take some time to get used to this new security measure, but eventually, it will become second nature. It’s an excellent investment and will ensure your site and its users remain safe and secure.
Got any questions? We’re happy to help! Click here to send in your questions.