Digital signatures are becoming more popular year on year. The digital signature market is poised to grow at a compound rate of 31% per annum by 2026 to a $14.1B market (MarketsandMarkets, 2020).
Not just because of the increased governance process but because of the improved document management workflow processes that products such as Formstack Documents can provide.

What are digital signatures? A digital signature is a more secure form of electronic signature that can render a document legally binding. It complies with strict regulations to ensure all parties involved of the signers’ identities.
The study from LunarPen in 2020 calculated the average time difference in obtaining business documents went from 5 days on average to 37 min (LunarPen, 2020).
A digital signature is now used because it helps build trust between merchants and clients even through an electronic medium.
It can be in the form of a typed name, a pasted signature picture, and a unique code to make the signing official. It is often placed on all the pages of an electronic contract or anything else that requires a signature.
To create a digital signature, you will need an input device. While your mouse or keyboard can adequately fulfill some applications’ requirements, a digital pen is the most flexible way of providing a legally binding signature.
Why are signatures required?
Contracts often need signatures to confirm the integrity of the document. These signatures verify the identity of the signers, thus increasing the level of trust between the parties involved. Whether a signature is digital or in actual written form, it should be legally binding. To make it legally binding, it should be an accurate representation of who the persons are.
It is crucial to have each person’s signature included in a contract to make each party involved accountable to the agreement. A signature shows that the person has read the terms and agrees with all of them. A document is rendered legal when all parties have signed the pages. There is an assumption that all parties have read all the pages.
So, it is recommended that documents should be studied in-depth before signing. Typically, signatures consist of a representation of a person’s name. Some signatures clearly show the full names, while others look more like squiggles. These days, though, even an x mark or a picture can be a form of signature. Of course, the signature should be an accurate representation of the signer.
How do digital signatures work?
On your end, you may only be familiar with the fact that you need a digital device to input your electronic signature. But what happens when you enter your information?
They go through authentication and encryption with public key infrastructure (PKI).
These processes are done to verify digital identity. PKI uses a pair of keys, a public one and a private one.
A mathematical algorithm is applied to these keys to create the needed authenticated digital identity.
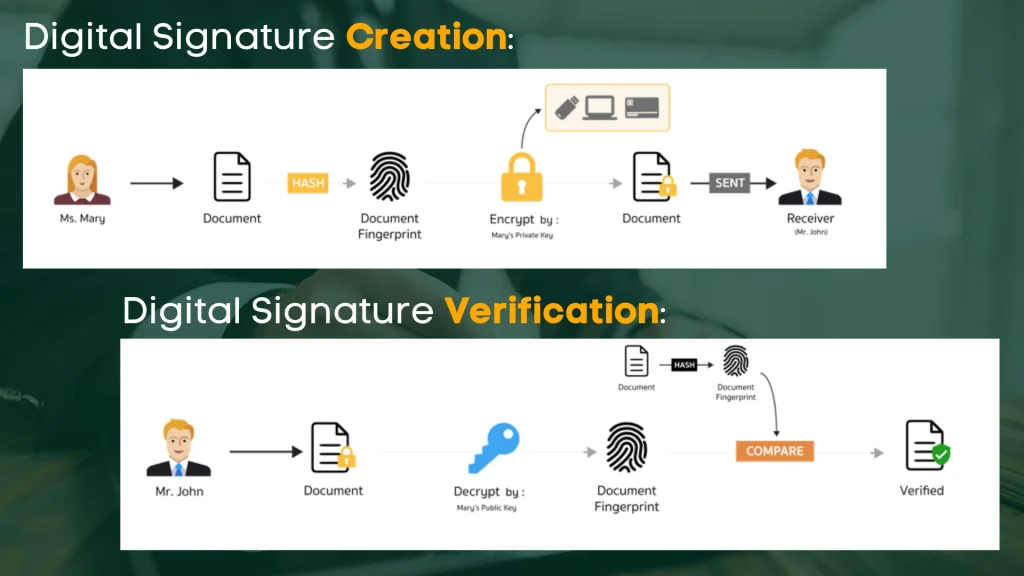
- First, the sender opens a file to sign. It can be in a document form that they must download, or it can be housed in a document platform.
- Then, the sender’s computer uses mathematical algorithms to find the contents’ hash value.
- The previous step is vital because the hash value must be encrypted with the sender’s private key. That encryption can produce the signature. The signature is applied to the file.
- The updated file is then sent to the receiver.
- The receiver opens the updated file using the appropriate application. The file can be identified as digitally signed. The sender’s public key has been used to help the receiver decrypt the key.
A digital signature is unique. If a person sells something online, they only share their public key with the buyer. They go into agreement with this buyer using their digital signature.
If someone else tries to communicate with the buyer, that person’s signature will not match the original person’s digital signature.
You are looking at two possibilities here:
- One, the first person has changed their signature, thus also changing their public key.
- Two, a different person is trying to communicate as the first person.
PKI provides the keys that protect the signature’s integrity. It ensures the security of transactions that incorporate the use of such keys. Therefore, the whole process should be overseen by a Certificate Authority (CA).
How many digital signature providers have you already encountered?
DocuSign, HelloSign, PandaDoc, and other popular digital signature providers had to meet PKI requirements to be operational.
What’s the difference between e-signatures and digital signatures?
Though the two may sound the same, they are not. As mentioned earlier, a digital signature has to go through mathematical processes to achieve security.

It also entails producing two types of keys (public and private) to authenticate a signer’s identity. The digital signature placed on a document can also indicate that a document has not been changed.
A digital signature is a more secure type of electronic signature. On the other hand, the term electronic signature is used more for a digitalized form of handwritten signature.
Whenever people hear “digital” or “electronic” used for a signature, they think of this particular type.
Digital signatures vs. electronic signatures
Here are some key differences between the two:
- The purpose differs. A digital signature secures a document, while an e-signature verifies it.
- Digital signatures have two processing platforms: Adobe PDF and Microsoft. Meanwhile, e-signatures have various types, including basic, click-to-sign, and qualified advanced.
- Basic – is the use of hand signature marks. It is a type of electronic signature. However, it is typically protected by a digital signature, as well, nowadays.
- Click-to-sign – is the use of prepared signatures that can be clicked or copied and pasted. It is usually not recommended to use them if not protected by a different level of security.
- Qualified Advanced – is the use of an electronic signature that can be directly linked to the person’s identity. The signature can be identified by anyone using an industry-standard PDF reader.
- The government-authorized digital signature is more secure than the merchant-authorized electronic signature.
- A certification authority regulates a digital signature, while some national acts regulate an electronic signature.
- Digital Signatures:
- They use public keys and encrypted methods, while an electronic signature is a generic expression. Again, a digital signature is a type of electronic signature, so some e-signatures are more secure than others. Refer to the three types of e-signatures above.
- Carry more information within it. It comes with links to the signer’s identity and has a timestamp. On the other hand, an electronic signature may not carry anything other than itself, depending on its classification.
- Make use of encryption specifically made for verifying the signer’s identity. On the other hand, an electronic signature may be verified by the usual phone and email address checks. Both have some level of security, but top companies require a digital signature for a good reason.
- Digital signatures prevent people from being impersonated online. For this reason, they are preferred over basic-level e-signatures when signing digital forms of legal documents.
Are digital signatures legal?
In general, digital signatures are legal, and the documents signed with them are enforceable. Usually, they don’t even need the encryption processes that form a digital signature to bind an electronic signature legally.

Nevertheless, digital signatures may still be required when dealing with regulated industries or in the European Union. The use of encrypted digital signatures is more common in the European Union.
To ensure the legality of digital signatures, check the application you are planning to use.
The platform should comply with eIDAS, ESIGN, and UETA. It should also comply with worldwide laws as the exchange of signatures may be done between two people from different countries.
As of the time of writing, more than a million customers use various e-signature platforms, such as Formstack Sign, DocuSign, or HelloSign.
We have reviewed each of the platforms here and have included an infographic to help guide you to the right e-signature platform.
They use it for legally binding documents because each digital signature can:
- Verify the identification of each signer
- Link signatures to the signer’s identification as well as to the e-papers signed
- Protect documents from tampering
- Record a person’s signed official electronic papers for monitoring
- Confirm the signer’s agreement with a document’s contents and intent to do the signing electronically
All electronic signatures can hold up in court if they can be authenticated. Therefore, digital signatures are still preferred over electronic signatures even if the former is not often required.
New platforms, however, are designed to ensure authentication. Using a reputable signature platform is recommended at all times.
Are digital Signatures safe and secure?
Typical security systems are in place.
It is normal to be concerned about whether your digital signature is secure or not. With some people’s identities getting stolen through the use of IDs and credit cards, a lot can be done on a person’s signature.
After all, it is your chosen means of identification when transacting legal documents. Even traditional handwriting can be forged. As mentioned earlier in this article, digital signatures are secure forms of electronic signatures. It is not executed by simply retrieving a file and using it to copy and paste on an e-document.
Instead, a lot of things happen when you execute a digital signature.
The asymmetric cryptography involved allows it to generate two keys, a public and a private one. The public key may be sent to another person for authentication.
However, the private key remains with the signatory. It is the private key that must be accessed for falsification to be done.
What are some of the software security processes that occur?
- The signatory signs the e-document.
- The signature is hashed.
- The signer’s private key encrypts the hash.
- The certificate and the signature are attached to the data.
- The final result is a digitally signed e-document.
- The digitally signed data goes through a verification process
- A hash function is applied to the data to generate the hash
- The signature is decrypted using the signer’s public key to get to the hash
- The two hashes are compared
- If the two are not the same, then a change must have occurred after the signing of the documents
Public key infrastructure (PKI) technology allows for the secure transfer of documents. It verifies the identity of the sender and checks the signature for authentication.
Without a public key, a person who is not supposed to receive the signature will not be able to decrypt the hash. The timestamps also make the signatures more difficult to forge.
PKI technology also allows for the transactions to identify the computer that sent the digital signature.
Of course, it cannot pinpoint the specific person seated at the computer at any given time, but secondary checks can be applied.
Two-factor authentication and offline corroboration may be used in some cases.
Note that the two hashes produced (one by decryption and one by applying a hash function) are compared. If the two do not match, then an alteration has occurred.
An alteration after the original signing invalidates the whole document.
So, if someone agrees and signs the document and tampering occurs after, the entire document is no longer acceptable.
You can see then that even if digital signatures are vulnerable to hacking attacks (intended to steal private keys), several software securities are in place.
These securities are present no matter where you are, as long as you choose a reputable digital signature platform.
Core Security Services Provided by Digital Signatures
Most providers offer the following security features:
- Signer authentication – Signer authentication means providing proof of who actually signed the document. Digital signatures link the signature to an identifiable entity.
- Non-repudiation – The signer cannot deny their signature on a document in question, and it guarantees that it can be proven the signer has indeed attached their signature. Conversely, it can be proven that someone did not affix their signature when they falsely claim they did.
- Data integrity – It can also be proven that the document has not been tampered with since signing.
Have you decided on a digital signature platform yet? Find out more about how digital signatures can speed up your quoting and sales processes. Such services also offer comprehensive business solutions covering workflow automation, contract analyzer, and quoting engine.
Top 5 considerations for signing online?
When you are signing documents online – especially for the first time – you need to consider a few things:
1. Your digital signature is legally binding.
Read the document carefully. Do not skip any line because signing it makes it legally binding. Therefore, you must be aware of all the details. The digital signature in itself does not have legal status, even though it makes the e-document enforceable. Instead, it provides identification, as well as encryption that secures it.
The encryption helps ensure the identification of the actual signatories. Therefore, it does have its hand in getting these e-documents approved as legally binding.
2. Signing all pages are not required.
When signing paper documents, you are often asked to sign your initials on all the pages. This requirement is meant to check whether you have read all the pages. It is not a requirement for digital documents. However, there will still be some instances where the other party may still require it. The best thing to do is to read all the pages and sign where asked to. Being extra careful with reading each page of the e-document benefits you, anyway. Digital signature platforms make the process convenient by quickly storing your signature after the first instance. Then, you only need to click on the succeeding boxes to affix that signature.
3. Storing signatures is possible.
Digital signature platforms can store your signatures. By doing this, they make it easy for you to sign other documents in the future. However, it is also a risk to have your signatures lying on the web somewhere. Therefore, you must make sure that you are dealing with a reputable source. The website should be secure.
4. Your computer and platform are key.
Continuing on the subject of security, you must choose a reputable platform in which you will sign your e-documents.
Make sure your browser and your computer are also safe from any intrusion and theft. You don’t want your private key ending up in the wrong hands. Once someone has your private key, they can take over your digital signature identity online. Fortunately, top digital signature platforms prevent this from happening.
5. It does not have to look like your signature.
Some people make an effort to sign their e-documents using an input device to create a digital signature that resembles their handwritten one. You do not have to do this. Digital signatures can take on several forms. They may be in the form of initials. In some cases, you only need to click on boxes to confirm your agreement with the document.
Summary
Digital signatures appear to be a way to adjust to the present and prepare for the future. What are digital signatures? A digital signature is more secure than an electronic signature as it provides an audit trail, an encrypted document, authentication and security for each recipient. It complies with strict regulations to ensure all parties involved of the signers’ identities. An electronic signature is a verification that the document has been signed by each of the parties but is still acceptable for signing certain contracts.
Their presence has made many business transactions quicker and more convenient. It does not matter if one company is in one country and the other is several thousand miles away in another country. Electronically signing documents has made global expansions and cooperation seamless and secure. It has also made business virtually mobile even with the current pandemic situation.